What is blood donation?
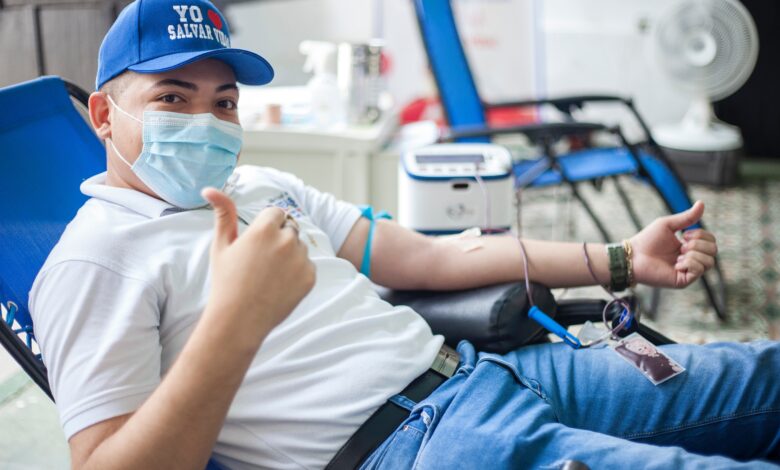
Blood donation consists of taking blood from a donor to transfuse it to a patient by blood transfusion. No treatment or medication can replace blood products. Some emergency situations also require blood transfusions such as accidents, childbirth, etc. Everyone can sooner or later need blood.
Blood donation, what is it?
Blood is made up of red blood cells, white blood cells, platelets and plasma. These different components all have their role and can be operated independently or not depending on the needs. The term “blood donation” actually includes three types of donation:
Whole blood donation. During this donation, all the elements of the blood are collected. A woman can give blood 4 times a year and a man 6 times. 8 weeks must separate each donation.
Plasma donation. To collect only plasma, the blood is filtered and the other blood components are returned directly to the donor. Plasma can be donated every 2 weeks.
The donation of platelets. Platelet donation works like plasma donation, only the platelets are collected and the other blood components are returned to the donor. Plates can only be kept for 5 days. Platelets can be given every 4 weeks and up to 12 times a year.
Blood donation, how does it work?
A blood donation usually takes place in the same way. After being received at the collection centre, the donor goes through several stages:
- The interview with the doctor : the donation candidate is systematically received by a doctor before his donation. This verifies his state of health, his personal and family history but also other elements such as a recent appointment with the dentist, his illnesses, his hospitalizations, whether or not he has a blood disease, his trips, etc It is at this time that we check the tension of the future donor but also that we calculate the volume of blood that we can take from him. This calculation is made according to its weight and size.
- The donation : it is made by a nurse. Sample tubes are taken before donation to perform various tests. It can last between 10 minutes (for whole blood donation) and 45 minutes for plasma and platelet donations.
- The snack: before, during and after the donation, drinks are offered to the donors. It is essential to drink a lot to help the body to compensate for the loss of liquid. A snack is offered to donors following the donation. This allows the medical team to “monitor” the donors after their donation and ensure that they are not tired or pale.
What are the contraindications to blood donation?
Only adults are allowed to donate blood. Some contraindications to blood donation exist such as:
- a weight of less than 50 kg,
- tiredness,
- anemia,
- diabetes,
- pregnancy: pregnant women or women who have recently given birth are not allowed to donate blood,
- taking medication: you must wait 14 days after the end of antibiotic or corticosteroid treatment ,
- a blood-borne disease (syphilis, viral hepatitis B and C or HIV ),
- an age greater than 70 in France and 71 in Canada.
Give blood, why?
It is important to know how a blood donation is organised, but it is all the more important to know what this blood is useful for. It is good to know that each year, 500,000 French patients are transfused and 500,000 patients use drugs derived from blood. In Canada, someone needs blood every minute, whether for treatment or for surgery. Knowing that with a single donation you can save up to three lives 1, the donation of blood must become a reflex and make it possible to treat and help ever more sick people. Whether it is to treat cancer patients, people affected by blood diseases (Thalassemia, sickle cell disease), severe burns or to save people suffering from haemorrhages, blood has many uses and will always be used to the best of its ability. But the needs are not being met and in many countries, although the number of donors is increasing 2 , voluntary donors are still being sought.